-->
- Disable Tcp Receive Window Auto-tuning Door
- Windows Tcp Tuning
- Tcp Receive Window
- Tcp Receive Window Settings
- Disable Tcp Receive Window Auto-tuning 2
Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel)
May 05, 2016 netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=highlyrestricted TCP Auto-tuning slow network performance. For the most part, I have seen the TCP Auto-tuning slow network performance issue come into play with new server OS’es and client OS’es talking to legacy server OS’es like Windows Server 2003.
Use the information in this topic to tune the performance network adapters for computers that are running Windows Server 2016 and later versions. If your network adapters provide tuning options, you can use these options to optimize network throughput and resource usage.
- Windows (Vista/7/8/etc) will automatically set - and more importantly, increase - the size of the TCP receive window for you, as needed, to maximize throughput. Receive Window Auto-Tuning: Microsoft calls this automatic management of the receive window size 'auto-tuning'.
- How to disable TCP chimney offloading and receive window autotuning in Windows Server, which may improve iSCSI network performance. TCP chimney offloading and receive window auto-tuning are frequently disabled as part of the process of troubleshooting a network-related issue on a Windows server.
The correct tuning settings for your network adapters depend on the following variables: Quick easy auto tune.
- The network adapter and its feature set
- The type of workload that the server performs
- The server hardware and software resources
- Your performance goals for the server
The following sections describe some of your performance tuning options.
Enabling offload features
Turning on network adapter offload features is usually beneficial. However, the network adapter might not be powerful enough to handle the offload capabilities with high throughput.
Important
Do not use the offload features IPsec Task Offload or TCP Chimney Offload. These technologies are deprecated in Windows Server 2016, and might adversely affect server and networking performance. In addition, these technologies might not be supported by Microsoft in the future.
For example, consider a network adapter that has limited hardware resources.In that case, enabling segmentation offload features might reduce the maximum sustainable throughput of the adapter. However, if the reduced throughput is acceptable, you should go ahead an enable the segmentation offload features.
Note
Some network adapters require you to enable offload features independently for the send and receive paths.
Enabling receive-side scaling (RSS) for web servers
RSS can improve web scalability and performance when there are fewer network adapters than logical processors on the server. When all the web traffic is going through the RSS-capable network adapters, the server can process incoming web requests from different connections simultaneously across different CPUs.
Important
Avoid using both non-RSS network adapters and RSS-capable network adapters on the same server. Because of the load distribution logic in RSS and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), performance might be severely degraded if a non-RSS-capable network adapter accepts web traffic on a server that has one or more RSS-capable network adapters. In this circumstance, you should use RSS-capable network adapters or disable RSS on the network adapter properties Advanced Properties tab.
To determine whether a network adapter is RSS-capable, you can view the RSS information on the network adapter properties Advanced Properties tab.
RSS Profiles and RSS Queues
The default RSS predefined profile is NUMAStatic, which differs from the default that the previous versions of Windows used. Before you start using RSS profiles, review the available profiles to understand when they are beneficial and how they apply to your network environment and hardware.
For example, if you open Task Manager and review the logical processors on your server, and they seem to be underutilized for receive traffic, you can try increasing the number of RSS queues from the default of two to the maximum that your network adapter supports. Your network adapter might have options to change the number of RSS queues as part of the driver.
Increasing network adapter resources
For network adapters that allow you to manually configure resources such as receive and send buffers, you should increase the allocated resources.
Some network adapters set their receive buffers low to conserve allocated memory from the host. The low value results in dropped packets and decreased performance. Therefore, for receive-intensive scenarios, we recommend that you increase the receive buffer value to the maximum.
Note
If a network adapter does not expose manual resource configuration, either it dynamically configures the resources, or the resources are set to a fixed value that cannot be changed.
Barbie cooking games free download for laptop. Welcome to Barbie.com! This fantastic destination has free online games for kids, online activities and fun online videos for kids! Check out our Barbie games, Barbie activities and Barbie videos. Share your Barbie printable activities with friends, download Barbie wallpapers and more!
Enabling interrupt moderation
To control interrupt moderation, some network adapters expose different interrupt moderation levels, different buffer coalescing parameters (sometimes separately for send and receive buffers), or both.
You should consider interrupt moderation for CPU-bound workloads. When using interrupt moderation, consider the trade-off between the host CPU savings and latency versus the increased host CPU savings because of more interrupts and less latency. If the network adapter does not perform interrupt moderation, but it does expose buffer coalescing, you can improve performance by increasing the number of coalesced buffers to allow more buffers per send or receive.
Performance tuning for low-latency packet processing
Many network adapters provide options to optimize operating system-induced latency. Latency is the elapsed time between the network driver processing an incoming packet and the network driver sending the packet back. This time is usually measured in microseconds. For comparison, the transmission time for packet transmissions over long distances is usually measured in milliseconds (an order of magnitude larger). This tuning will not reduce the time a packet spends in transit.
Following are some performance tuning suggestions for microsecond-sensitive networks.
Set the computer BIOS to High Performance, with C-states disabled. However, note that this is system and BIOS dependent, and some systems will provide higher performance if the operating system controls power management. You can check and adjust your power management settings from Settings or by using the powercfg command. For more information, see Powercfg Command-Line Options.
Set the operating system power management profile to High Performance System.
Dev c++ failed to execute error 5. Note
This setting does not work properly if the system BIOS has been set to disable operating system control of power management.
Enable static offloads. For example, enable the UDP Checksums, TCP Checksums, and Send Large Offload (LSO) settings.
If the traffic is multi-streamed, such as when receiving high-volume multicast traffic, enable RSS.
Disable the Interrupt Moderation setting for network card drivers that require the lowest possible latency. Remember, this configuration can use more CPU time and it represents a tradeoff.
Handle network adapter interrupts and DPCs on a core processor that shares CPU cache with the core that is being used by the program (user thread) that is handling the packet. CPU affinity tuning can be used to direct a process to certain logical processors in conjunction with RSS configuration to accomplish this. Using the same core for the interrupt, DPC, and user mode thread exhibits worse performance as load increases because the ISR, DPC, and thread contend for the use of the core.
Disable Tcp Receive Window Auto-tuning Door
System management interrupts
Many hardware systems use System Management Interrupts (SMI) for a variety of maintenance functions, such as reporting error correction code (ECC) memory errors, maintaining legacy USB compatibility, controlling the fan, and managing BIOS-controlled power settings.
The SMI is the highest-priority interrupt on the system, and places the CPU in a management mode. This mode preempts all other activity while SMI runs an interrupt service routine, typically contained in BIOS.
Unfortunately, this behavior can result in latency spikes of 100 microseconds or more.
If you need to achieve the lowest latency, you should request a BIOS version from your hardware provider that reduces SMIs to the lowest degree possible. These BIOS versions are frequently referred to as 'low latency BIOS' or 'SMI free BIOS.' In some cases, it is not possible for a hardware platform to eliminate SMI activity altogether because it is used to control essential functions (for example, cooling fans).
Note
The operating system cannot control SMIs because the logical processor is running in a special maintenance mode, which prevents operating system intervention.
Performance tuning TCP
You can use the following items to tune TCP performance.
TCP receive window autotuning
In Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and later versions of Windows, the Windows network stack uses a feature that is named TCP receive window autotuning level to negotiate the TCP receive window size. This feature can negotiate a defined receive window size for every TCP communication during the TCP Handshake.
In earlier versions of Windows, the Windows network stack used a fixed-size receive window (65,535 bytes) that limited the overall potential throughput for connections. The total achievable throughput of TCP connections could limit network usage scenarios. TCP receive window autotuning enables these scenarios to fully use the network.
For a TCP receive window that has a particular size, you can use the following equation to calculate the total throughput of a single connection.
Total achievable throughput in bytes = TCP receive window size in bytes * (1 / connection latency in seconds)
For example, for a connection that has a latency of 10 ms, the total achievable throughput is only 51 Mbps. This value is reasonable for a large corporate network infrastructure. However, by using autotuning to adjust the receive window, the connection can achieve the full line rate of a 1-Gbps connection.
Some applications define the size of the TCP receive window. If the application does not define the receive window size, the link speed determines the size as follows:
- Less than 1 megabit per second (Mbps): 8 kilobytes (KB)
- 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps: 17 KB
- 100 Mbps to 10 gigabits per second (Gbps): 64 KB
- 10 Gbps or faster: 128 KB
For example, on a computer that has a 1-Gbps network adapter installed, the window size should be 64 KB.
This feature also makes full use of other features to improve network performance. These features include the rest of the TCP options that are defined in RFC 1323. Adobe audition sound effects. By using these features, Windows-based computers can negotiate TCP receive window sizes that are smaller but are scaled at a defined value, depending on the configuration. This behavior the sizes easier to handle for networking devices.
Note
You may experience an issue in which the network device is not compliant with the TCP window scale option, as defined in RFC 1323 and, therefore, doesn't support the scale factor. In such cases, refer to this KB 934430, Network connectivity fails when you try to use Windows Vista behind a firewall device or contact the Support team for your network device vendor.
Review and configure TCP receive window autotuning level
You can use either netsh commands or Windows PowerShell cmdlets to review or modify the TCP receive window autotuning level.
Note
Unlike in versions of Windows that pre-date Windows 10 or Windows Server 2019, you can no longer use the registry to configure the TCP receive window size. For more information about the deprecated settings, see Deprecated TCP parameters.
Note
For detailed information about the available autotuning levels, see Autotuning levels.
To use netsh to review or modify the autotuning level
To review the current settings, open a Command Prompt window and run the following command:
The output of this command should resemble the following:
To modify the setting, run the following command at the command prompt:
Windows Tcp Tuning
Note
In the preceding command, <Value> represents the new value for the auto tuning level.
For more information about this command, see Netsh commands for Interface Transmission Control Protocol.
To use Powershell to review or modify the autotuning level
To review the current settings, open a PowerShell window and run the following cmdlet.
The output of this cmdlet should resemble the following.
To modify the setting, run the following cmdlet at the PowerShell command prompt.
Note
In the preceding command, <Value> represents the new value for the auto tuning level.
For more information about these cmdlets, see the following articles:
Autotuning levels
You can set receive window autotuning to any of five levels. The default level is Normal. The following table describes the levels.
| Level | Hexadecimal value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Normal (default) | 0x8 (scale factor of 8) | Set the TCP receive window to grow to accommodate almost all scenarios. |
| Disabled | No scale factor available | Set the TCP receive window at its default value. |
| Restricted | 0x4 (scale factor of 4) | Set the TCP receive window to grow beyond its default value, but limit such growth in some scenarios. |
| Highly Restricted | 0x2 (scale factor of 2) | Set the TCP receive window to grow beyond its default value, but do so very conservatively. |
| Experimental | 0xE (scale factor of 14) | Set the TCP receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios. |
If you use an application to capture network packets, the application should report data that resembles the following for different window autotuning level settings.
Autotuning level: Normal (default state)
Autotuning level: Disabled
Autotuning level: Restricted
Autotuning level: Highly restricted
Autotuning level: Experimental
Deprecated TCP parameters
The following registry settings from Windows Server 2003 are no longer supported, and are ignored in later versions.
Tcp Receive Window
- TcpWindowSize
- NumTcbTablePartitions
- MaxHashTableSize
All of these settings were located in the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Windows Filtering Platform
Tcp Receive Window Settings
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 introduced the Windows Filtering Platform (WFP). WFP provides APIs to non-Microsoft independent software vendors (ISVs) to create packet processing filters. Examples include firewall and antivirus software.
Note
A poorly-written WFP filter can significantly decrease a server's networking performance. For more information, see Porting Packet-Processing Drivers and Apps to WFP in the Windows Dev Center.
Disable Tcp Receive Window Auto-tuning 2
For links to all topics in this guide, see Network Subsystem Performance Tuning.
Some networking devices, such as SPI firewalls, some NAT routers, VPN endpoints, WiFi devices have problems with the way Windows Vista resizes the TCP Window. Possible symptomps include: web traffic ok, email timeouts on receiving only, slow or no network file server access, random network timeouts or connectivity problems, freezing or slow web browsing or VPN connections.
Note that disabling TCP Window autotunning limits the TCP Window to 65535, which may not be adequate for faster broadband internet connections.
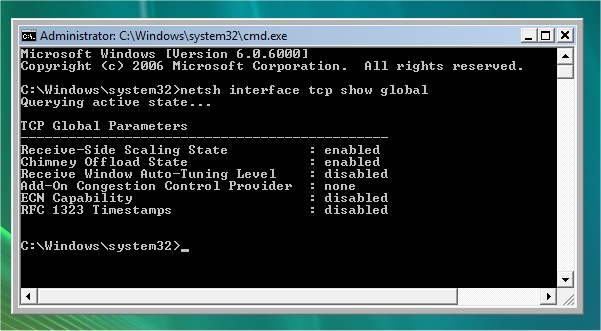
To disable TCP/IP autotunning, in 'Elevated' Command Prompt type:
netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=disabled
To verify that it is dsabled:
netsh interface tcp show global
To set back to the default Windows Vista behavior:
netsh interface tcp set global autotuningl=normal
Windows has the ability to automatically overwrite the above user settings, so you may also want to enforce them with the following: netsh int tcp set heuristics disabled (for more information, see Windows 7/Vista Tweaks article)
Note: To get elevated command prompt (admin priviledges), you may need to do the following:
- Click the Start button
- In the Search box, type: Command Prompt
- Right-click on the Command Prompt icon and select 'Run as administrator'
Note: You can also change the default auto-tunning behavior in other ways, for example typing this in command prompt: netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=highlyrestricted
The above command helps with servers that do not fully support RFC 1323. See: MSKB929868
See also:
Windows Vista Elevated Command Prompt
Windows 7 Tweaks
rate: avg: need help with this tweaking!!!! error message keeps coming up that says 'Set global command failed on IPv4 The requested operation requires elelvation' ????? In the TCP Optimizer FAQ's section, Windows Vista is not listed as a supported operating system. This post indicates that TCP Optimizer WILL work with Windows Vista. So, will TCP Optimizer work with Windows Vista or not? If it can, is it possible to add Windows Vista to that particular FAQ about operating system support for TCP Optimizer?? Ok, I found out how to do this in Vista. Go to 'Start' then 'All Programs', then 'Accesories' and right click on 'Command Prompt', and select 'Run as administrator'. Enter the command just as in the post, and you will no longer recieve that elevation message. Can Anyone Tell Me How Change The RWIN Value On Vista. The Analiser Says It Can Be Improved To Provide A Faster Speed. Bonjour à tous, j'ai le message d'erreur suivant : Impossible de charger la DLL application d'assistance suivante : P2PNETSH.DLL. Si qq'un à une idée .. I disabled and checked it, I still can't run Fios Optimize Hi, can someone tell me if I can tweak my connexion to a hotspot (I'm connected to a free Fon Hotspot and I can't have more than 600 Kbps). Please answer.. DO NOT DISABLE AUTOTUNING IN VISTA!!! koz it rejects tweaking all life-meaning tweaks, like MTU auto discovery etc. Check this out - turn off autotuning, reboot, change some parameter like MTU, RWIN, remember it, then reboot and go to the registry. You can see that all parameters you've changed before rebooting are reverted to the default state !!!!!! I got ADSL Unlimited 340k and all is working fine without disabling autotuning You need to run Command Prompt as an Administrator. Type 'command' in the search box in the Start Menu and then right click Command Prompt and Run as Administrator and then type/paste the above in and it will work. Thank you so much for this information about disabling autotuning. I was being timed out every minute or so on webmail and tried several solutions. This is the one that solved it. ty work great for me i have disabled it for test and later i find this slow down all other connection i have at same time netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=highlyrestricted worked good work. in windows 7 !! I disabled auto tuning in vista and rebooted.But , state is still showing as 'highly restricted' This helped me with immense lag in TF2. I was playing a less demanding game for a while and 7 autotuned to it. Autotuning needs to die altogether. I need to disable 2420:TCP so that I can pass my PCI Compliance scan for my online credit card virtual terminal. Can you help? If just the RWIN Scaling could be set manually to anything else than 0 bits. I managed it to get RWIN 64768 at MTU 1448, that's MSS*46 on Windows 7 Is there a way to permanantly disable auto-tuning in windows 7? I ran the elevated command prompt and verified it was disabled, but when I rebooted, it was set to normal again. Try to add store=persistent add the end of the netsh.exe command 1. Try to make a non-HTTP network connection. That is, use the program that was affected by the problem. 2. If the problem is fixed, contact the manufacturer of the firewall device for steps to resolve the issue. 3. You can keep auto-tuning disabled until the problem is fixed. When you are ready to enable auto-tuning, click Start, click All Programs, click Accessories, and then click Command Prompt. 4. At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER: netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=normal This command enables Receive Window Auto-Tuning again so that you can take advantage of the increase in network throughput performance that this option provides. very nice bot at WIN7 german it was interface tcp set global autotuninglevel={disabled/normal} It W7, theres 5 level of Auto Tuning can be set 1. Disabled Disable the autotunning feature in Vista completely、and fit and lock the RWIN receive window to default value 65,536 bytes. Enter: netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled 2. HighlyRestricted Allow for the receive window to grow beyond the default value、but do so very conservatively. In this mode、Vista will by default use RWIN of 16,384 bytes with a scale factor of 2. Enter: netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=highlyrestricted 3. Restricted Allow the receive window to grow beyond its default value、but limit such growth in some scenarios. Enter: netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=restricted 4. Normal (Windows 7,Server 2008,and Vista's Default setting) Allow for the receive window to grow to accommodate almost all scenarios. The default setting in Vista. Specifying this command mean you want to turn back on AutoTuning feature. Enter: netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=normal 5.Enter Experimental Allow for the receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios. Note The experimental value can decrease performance in common scenarios. This value should be used only for research purposes. Enter : netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=experimental dude see the above description. it clearly says that you need administrator priveleges. It means exactly what it says: you need elevated permissions. You must be an administrator. after that i modified the parameters, it's requires restart the system?? In order to disable AutoTuning via a script for a domain, the script needs to be run as a Startup script not a Logon Script. Startup scripts run with Elevated Permission in Windows 7. |